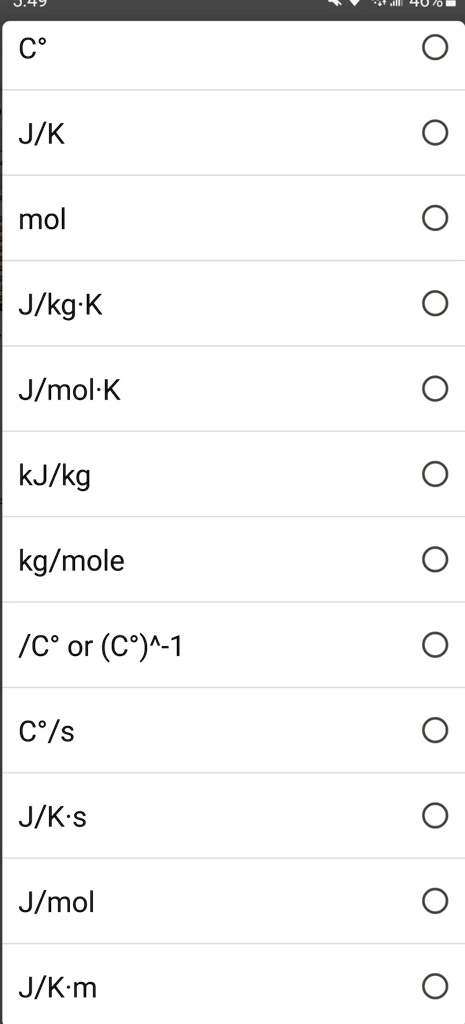
36.) Calculate the rms speed of an ideal diatomic gas having molecular weight 32 gm/mol at Oc If the specific heats at constant pressure and volume are respectively 29.1 J mol1 K

Three moles of an ideal gas are taken around the cycle abc shown in the figure. For this gas, C_ p = 29.1\ \frac{J}{mol.K}. Process ac is at constant pressure, process ba
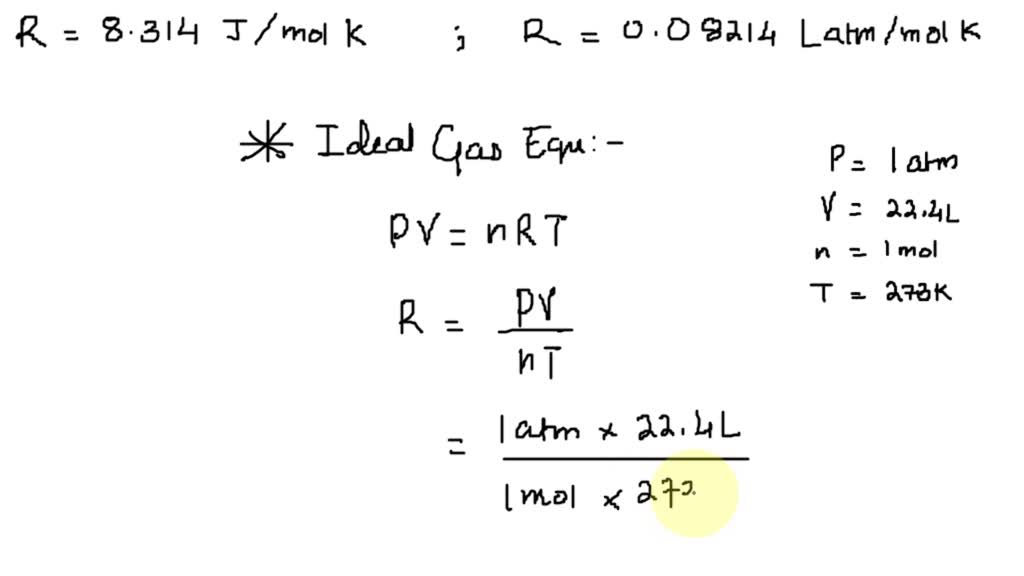
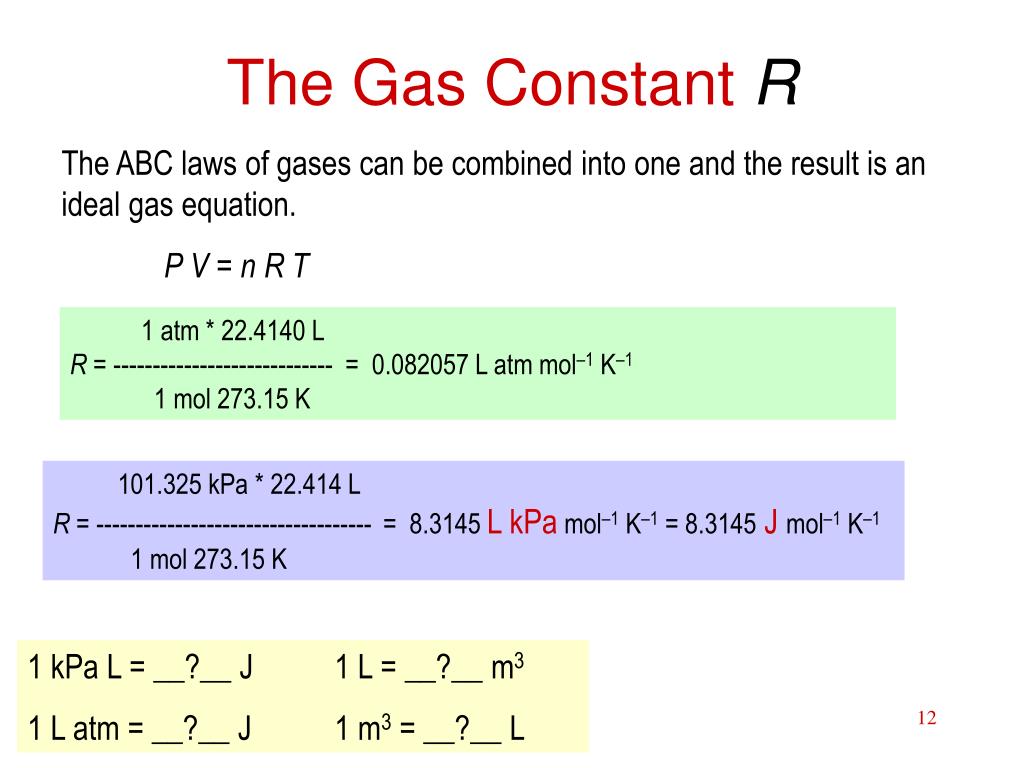
SOLVED: The universal gas constant; R 8.314 J/mol. K In other unit system; R = 0.08214 Latm/ mol. K Using unit conversion, show how the first value for R can be converted

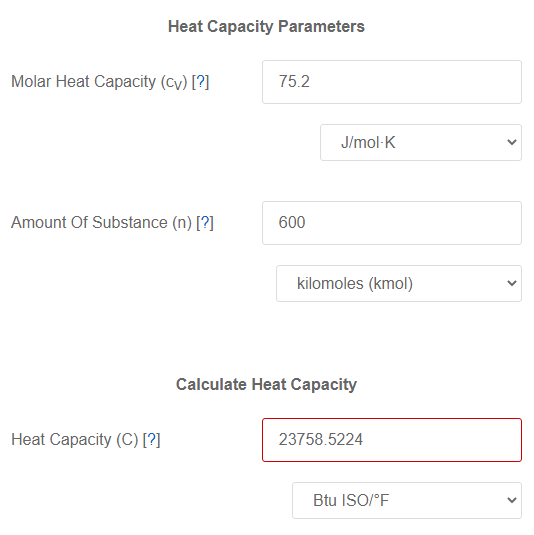
Calculate the number of kj necessary to raise the temperature of 60 g of Aluminium from 35 to 55°C. Molar heat capacity of A1 is 24 J ${{mol }^{-1}}$${{K}^{-1}}$ - CBSE Class 11
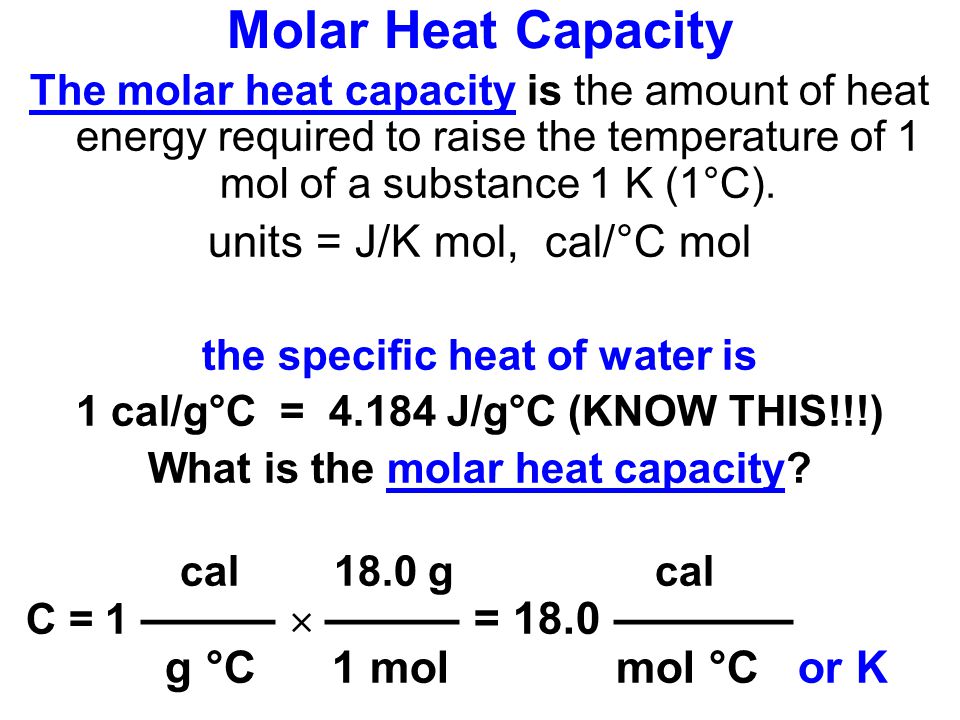
Goals of Chapter Assess heat transfer associated with changes in temperature and changes of state. Apply the First Law of Thermodynamics. Define and understand. - ppt download

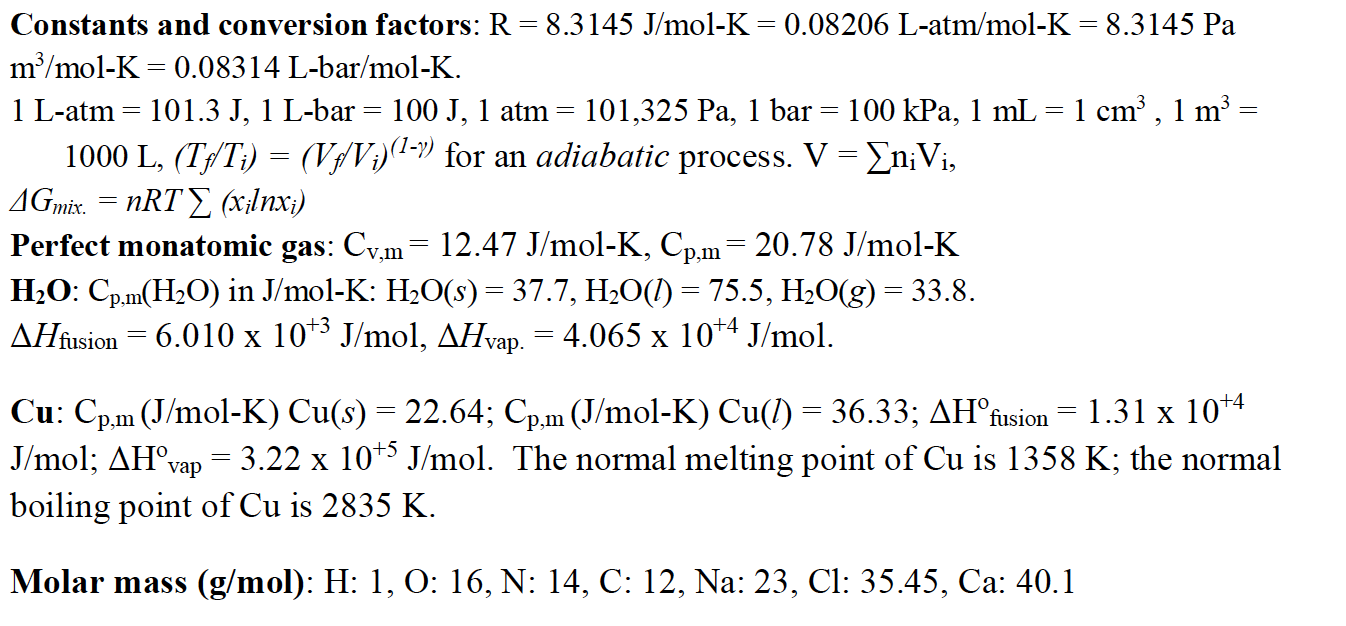
SOLVED: USEFUL CONSTANTS R = 8.314 J/mol/K = 0.08205 Latm/mol/K kB = 1.38 x 10^-23 J/K h = 6.626 x 10^-34 s c = 3 x 10^8 m/s 1 cm^-1 = 1.98 x 10^-23 STP = 298 K, 1 bar (10^5 N/m^2)




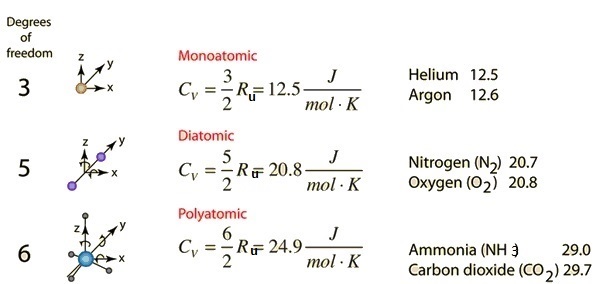
![ANSWERED] What is the internal energy of 7.00 mol o... - Physical Chemistry - Kunduz ANSWERED] What is the internal energy of 7.00 mol o... - Physical Chemistry - Kunduz](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/52923887-1659262298.2603226.jpeg)